
What are SDS and Non-SDS Application that students need to understand to apply for studying in Canada?
Canada has emerged as a highly preferred destination for international students seeking to study abroad. Various surveys indicate a significant rise in the number of students opting for Canada as their top choice over other English-speaking countries like Australia, the USA, and the UK. This growing popularity of Canada has resulted in an increase in the number of applications from students aspiring to study in Canadian institutions.
These applications can be broadly categorized into SDS (Student Direct Stream) and non-SDS. Students must understand the distinction between these categories and determine the most suitable for their visa application, ensuring the best chances of success.
SDS, previously known as the Student Partner Programme (SPP), is one category under which students can apply for admission to universities or colleges in Canada. On the other hand, the non-SDS category encompasses applications that do not fall under the SDS criteria.
What is SDS?
The Canadian government has implemented the Student Direct Stream (SDS) program to expedite the application process for international students seeking admission to post-secondary designated learning institutions (DLIs) in Canada. This initiative aims to reduce processing times significantly. If all the eligibility requirements are satisfied, the majority of SDS applications are processed by the Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) within a period of 20 calendar days. The SDS is available to legal residents who also reside in 14 countries including India.
To be eligible for SDS processing, applicants must fulfill specific requirements by submitting the following documents:
Valid Language Test Result
Students must provide a proof of a valid language test completed within the 2 years from when the SDS application was received. Acceptable scores include an IELTS score of 6.0 or higher in each language skill (listening, reading, writing, and speaking) or a TEF score equivalent to a CLB score of at least 7 for each ability.
With a recent update in the policy, students can now apply under the SDS category using any of the new IRCC-accepted tests to prove English language proficiency, such as CELPIP General, CAEL, PTE Academic, and the TOEFL iBT Test. This implementation will be effective on August 10, 2023.
Valid Passport
To apply for a student visa in Canada, students must possess a valid passport. It is essential to ensure that the passport's expiration date is not imminent, as Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) will not issue the study permit, temporary resident visa (TRV), or any other necessary documents if the passport is expired or nearing expiration. Maintaining a valid passport is crucial for a smooth and successful visa application process.
Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC)
Canada study visa applicants must submit proof of a GIC worth CAN$10,000 or more from a bank insured by CDIC or listed on the IRCC SDS webpage. The GIC should meet certain conditions, such as funds being held in an inaccessible account until the applicant's arrival in Canada. Funds are disbursed in installments over 10 to 12 months, with the initial disbursement upon the applicant's entry and subsequent payments on a monthly or bimonthly basis.
Proof of Tuition Payment
the applicants also need to show evidence of full payment of tuition for the first year of study. This can be in the form of a receipt or official letter from the designated learning institution (DLI) confirming payment. Alternatively, proof of funds transferred to a repository account at the DLI for future tuition payment is also acceptable.
Other Supporting Documents
Include a letter of acceptance from a post-secondary DLI, the most recent educational transcript, and proof of completion of a medical examination from a panel physician, particularly for applicants who have spent 6 months in designated countries or territories or whose field of study requires upfront medical examination results.
By submitting these required documents, applicants demonstrate their eligibility for SDS processing.
List of SDS colleges in Canada by province
- Alberta
- Quebec
- Manitoba
- Ontario
- British Columbia
- Nova Scotia
- New Brunswick
- Saskatchewan
- Prince Edward Island
- Newfoundland and Labrador
What is Non-SDS?
For students who are unable to meet the specific requirements of the Student Direct Stream (SDS), there is an alternative option to apply for a student visa to study in Canada under the Non-SDS category. The Non-SDS category offers a standard visa application process that allows students to obtain temporary residency in Canada for their studies.
The Non-SDS category is designed for international students from all countries who do not qualify for SDS. It provides a pathway for students who may not meet the streamlined criteria of SDS but still meet the general eligibility requirements for studying in Canada.
Here are the requirements for the Non-SDS category for studying in Canada in 2023, explained in a different and improved way:
Language Proficiency Test
Non-SDS applicants must demonstrate their language proficiency by taking tests such as IELTS, PTE, or TOEFL. Clearing these tests helps prove their ability to communicate effectively in English or French.
Passport
Candidates need a valid passport to apply for a student visa in Canada. It is crucial to ensure that the passport is not expired as Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) will not issue a temporary resident visa (TRV) or a study permit if the passport has expired.
Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC)
As part of the financial requirements, students may need to deposit around $10,000 CAD or more in a Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC). This serves as a financial resource to cover initial expenses in Canada. Banks like NOVA SCOTIA,
ICICI, CIBC, and SBI offer GIC services. Alternatively, students can provide proof of liquid funds instead of a GIC.
Tuition Fee
Non-SDS applicants must demonstrate that they have paid the tuition fees for six months to the Designated Learning Institution (DLI) they plan to attend. This showcases their financial stability and commitment to pursuing their studies.
Medical Examination
Students are required to undergo a medical examination and submit the documentation as proof of their overall health and well-being.
Educational Documents
Genuine academic documents, such as certificates for 10th grade, 12th grade, graduation, or diplomas, must be submitted to validate the educational background and qualifications of the applicant.
Digital Pictures
Applicants need to provide digital pictures that meet specific specifications, including dimensions of 35x45 and an 80% zoom-in with a white background.
Statement of Purpose
A Statement of Purpose (SOP) is a crucial component of the application, where students explain their reasons for choosing Canada as their education destination and their specific course of study.
Financial Documents
Non-SDS applicants must submit financial documents to demonstrate their financial stability. These may include Proof of Income, such as Income Tax Returns, Form-16, or J-Forms, as well as evidence of liquid assets like Government Provident Fund (GPF), bank statements, fixed deposits, and other relevant financial resources.
It's important to note that these requirements may be subject to change and can vary based on individual circumstances and the specific policies of the Canadian immigration authorities. Therefore, it is advisable to refer to the official Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) website or consult with the chosen Canadian educational institution or a qualified immigration consultant for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the Non-SDS category requirements.
There are several compelling reasons why choosing the Student Direct Stream (SDS) program over the Non-SDS category is often considered advantageous. Here are some key points:
Expedited Processing
SDS offers faster processing time, making the overall application process more efficient. On average, SDS applications are processed within approximately 20 days, provided that all the specified program requirements are met. This swift processing is particularly beneficial for students who wish to begin their studies at the earliest opportunity.
The success rate of non-SDS visa applications is relatively lower compared to those of the SDS category. According to the Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC), the success rate for SDS applicants in 2021 stood at 71%, whereas it was 40% for non-SDS applicants. By opting for the SDS program, students can benefit from a streamlined application process with simplified documentation requirements. This not only saves time and effort but also allows for a quicker transition to their chosen college or university in Canada.
What is the difference between SDS and Non-SDS visa applications?
|
SDS Visa |
Non-SDS visa |
|
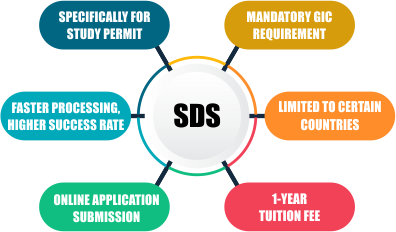
Specifically for Study Permit: SDS visa is applicable only for obtaining a study permit to study in Canada. |
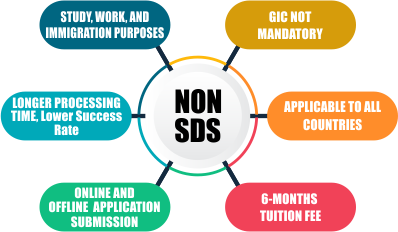
Study, Work, and Immigration Purposes: Non-SDS visa is suitable for those seeking a Canada Study Permit, Work Permit, or immigration purposes. |
|
Faster Processing: The visa application under SDS is processed within 20 days on average, providing a quicker response time. |
Longer Processing Time: Non-SDS visa applications may take between 45 to 90 days for processing. |
|
Online Application Submission: SDS applications are submitted online through the designated platform. |
Online and Offline Application Submission: Non-SDS applicants have the option to submit their applications either online or offline. |
|
Mandatory GIC Requirement: A Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC) of at least CAD 10,000 is a mandatory requirement for SDS applicants. |
GIC not Mandatory: Unlike SDS, a Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC) is not a mandatory requirement for Non-SDS applicants. |
|
Limited to Certain Countries: SDS is applicable to candidates from certain Asian and African countries as specified by the Canadian government. |
Applicable to All Countries: Non-SDS visa is open to candidates from any country. |
|
Higher Success Rate: SDS applications have a success rate of up to 85%. |
Lower Success Rate: Non-SDS applications have a success rate of up to 65%. |
|
1-Year Tuition Fee: SDS applicants are generally required to pay the tuition fee for one year in advance. |
6-Months Tuition Fee: Non-SDS applicants are generally required to pay the tuition fee for six months in advance. |
If you are considering studying in Canada and find yourself uncertain about which SDS or Non-SDS category is most suitable for your study visa application, we offer a complimentary counseling session with our team of study visa experts. Our experts will provide personalized guidance based on your academic profile, specific requirements, and individual circumstances to help you make an informed decision. To schedule your free counseling session and commence your study visa process promptly, please contact us at 92563-92563. We are here to assist you every step of the way.
Read our other Blogs
Related Articles
Study in UK With or Without IELTS: A Gateway to Global Education
Want to dream about studying in the UK, but apprehensive about an IELTS score? The good news is, you can
Financial Planning for Canada: Meeting the New Requirements with Ease
Studying in Canada has been a dream of many students all over the world due to
Most Popular Programs to Study in Australia
Making the right decision after finishing school may be overwhelming, particularly when
Why More Students Are Choosing New Zealand for Study Abroad
For a student, making the choice to study abroad is one of the
